|
Diabetes is a lifelong condition which can cause foot problems. Foot problems in diabetes are often caused by nerve damage and/or damage to the blood vessels. Blood vessels play a key role in transporting glucose and insulin throughout the body. It can be damaged through the effects of high blood glucose levels which in turn cause damage to organs, such as the heart, feet and eyes. High blood sugars over the long period of time affect the blood vessels and nerves which reduces the blood flow, especially in legs and feet. Damaged blood vessels will not transport as much blood as undamaged ones. If the blood vessels supply to feet are either clogged up or completely blocked the skin and flesh of the feet will suffer.
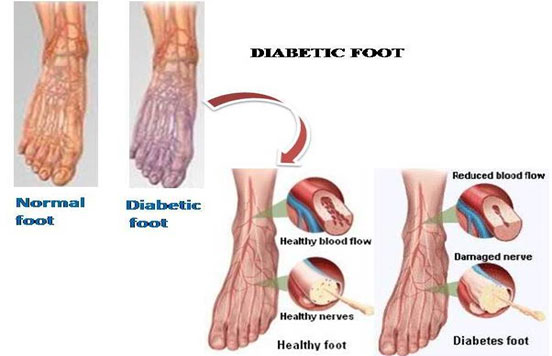
Nerves perform many jobs in human body, some of which are quite complicated. One of the most important things nerves do is to give feeling / sensation. Being able to feel things protects us from getting injured. People with diabetes sometimes develop nerve damage in the feet, which results in a range of different problems. One of the most serious problems is either the whole, or part, of feet can become numb or insensitive to pain, hence they fail to realize when they have a sore on their foot. The sore can become infected, the infection can spread when left untreated, and may requires amputation to reduce the spreading of further infection. Hence it is important to have regular foot exams done by a podiatrist. According to American Diabetes Association one in five people with diabetes who seek hospital care do so for foot problems.
The loss of sensation in feet due to diabetes can result in unnoticed pressure or injury. Incorrect footwear can increase the pressure on feet, which cannot feel. Normal injuries like nicks, cuts, bruises or blisters may go unnoticed and progress into ulcers. Then, the lack of blood flow caused by the diabetes decreases the body's ability to heal. Diabetic foot ulcers are often painless, but may take weeks or even several months to heal, and are the most common reason for hospital stays for people with diabetes. Left untreated, they are a common cause for surgical amputations. Most of the diabetic foot ulcers can be prevented or healed quickly if they are treated at early stages.

Any person might get corns, blisters, and other foot problems, perhaps patients with diabetes are more prone to foot problem due to uncontrolled blood sugar and blood pressure.
Corns & calluses:
These are the thick layer of skin due to excessive rubbing or pressure on the same area and can become infected.
Blisters:
Wearing shoes without socks and ill-fitting shoes can cause blister, which can lead to infection.
Ingrown toenails:
It will happen when edges of the nail grows in to the skin. Due to this skin become red and infected. It can happen if we cut into the corners of toenails while trim and wearing tight shoes.
Bunion:
It forms when your big toe slants toward the small toes and the place between the bones near the base of your big toe grows big. This spot can get red, sore, and infected. Pointed shoes may cause bunions. Bunions often run in the family.
Hammertoes:
This is form due to the weak foot muscle as a result of Diabetic nerve damage. The weakened muscle makes the tendons in the foot shorter and makes the toes curl under the feet. The feet can change their shape, which can hamper the walking. Wearing shoes that are too short can also cause hammertoes.
Dry and cracked skin:
This can happen when nerves in the legs and feet do not get the message to keep our skin soft and moist. Dry skin can become cracked, which allows germs to enter and cause infection. If blood glucose is high, it feeds the germs and makes the infection worse.
Athlete's foot:
It is a fungus that causes itchiness, redness, and cracking of the skin. The cracks between the toes allow germs to get under the skin and cause infection. The infection can spread to the toenails and make them thick, yellow, and hard to cut
The most essential components of foot management are:
(a) Regular inspection and examination of the at-risk foot, (b) Identification of the at-risk foot and (c) Treatment of ulcers and infections.
Apart from glycemic control, an appropriate dietary pattern and management of personal habits plays a major role. Further in order to manage neuropathic foot, a prompt and regular inspection and examination of the neuropathic foot and treatment of deformities, ulcers, and infections are required.


Although we often take them for granted, our feet are a very important part of our body. If a person is having diabetes, they have a greater chance of developing foot problems. Serious foot problems can often be prevented from damage to nerves and blood vessels. To prevent one can maintain healthy blood glucose levels, blood pressure, blood lipid levels (cholesterol), taking good care of feet every day and keeping in close contact with doctor or podiatrist if in case of foot problem. Further smoking cessation, staying active, regular exercise and maintaining a healthy body weight also helps to prevent these damages.
Smoking can bring on illness associated with diabetes earlier, causing disability and death. People with diabetes who smokes, have increased blood-sugar levels than nonsmokers with diabetes. Smoking affects blood circulation by increasing heart rate and blood pressure and by making small blood vessels narrower. It also makes blood cells and blood-vessel walls sticky, and allows dangerous fatty material to build up. This can lead to heart attack, stroke and other blood vessel disease. People with diabetes have a greater chance of develop life threatening kidney and heart disease among smokers than non smokers. Hence quitting smoking is one of the best things to manage diabetes and stay healthier for longer.
The steps that the diabetic patient should follow for cutting the toe nails are:
Proper footwear is an important part of an overall treatment program for people with diabetes, even for those in the earliest stages of the disease. Patients with diabetes should not use footwear with toe grip or toe rings to hold on. It is always advisable to use sandals inside and outside the house. Avoid like Hawi chappals and foot wares made of nylon or plastic, leather footwear breathes better than any other materials. Footwear should be fastened with an adjustable lace, strap or Velcro. Ideally footwear should be purchased in the evenings because the feet swell a little during the day time. The heel of the footwear should not be more than 1 inch. If it is more there will be increased pressure on the ball of the feet. This is the area where ulcers develop more frequently.
By taking active precautions under the care of a medical professional, future problems can be avoided. Remember, shoes correctly fitted by a foot care specialist, appropriate exercise and diet, and regular medical care will go a long way toward helping peoples with diabetes stay healthy, comfortable, mobile and happy life.
